45 adenosine triphosphate (atp) is a molecule that provides energy for cellular functions. label the three major components of an atp molecule.
What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic Adenine, Ribose, and three Phosphate groups. ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine Ribose Three Phosphate Groups Here is a picture: adenosine triphosphate | Definition, Structure, Function, & Facts Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, is the primary carrier of energy in cells. The water-mediated reaction known as hydrolysis releases energy from the chemical bonds in ATP to fuel cellular processes. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. See all videos for this article
ATP Synthase - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictionary ATP is the main energy molecule used in cells. ATP synthase forms ATP from adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and an inorganic phosphate (P i) through oxidative phosphorylation, which is a process in which enzymes oxidize nutrients to form ATP. ATP synthase is found in all lifeforms and powers all cellular activities. Function of ATP Synthase
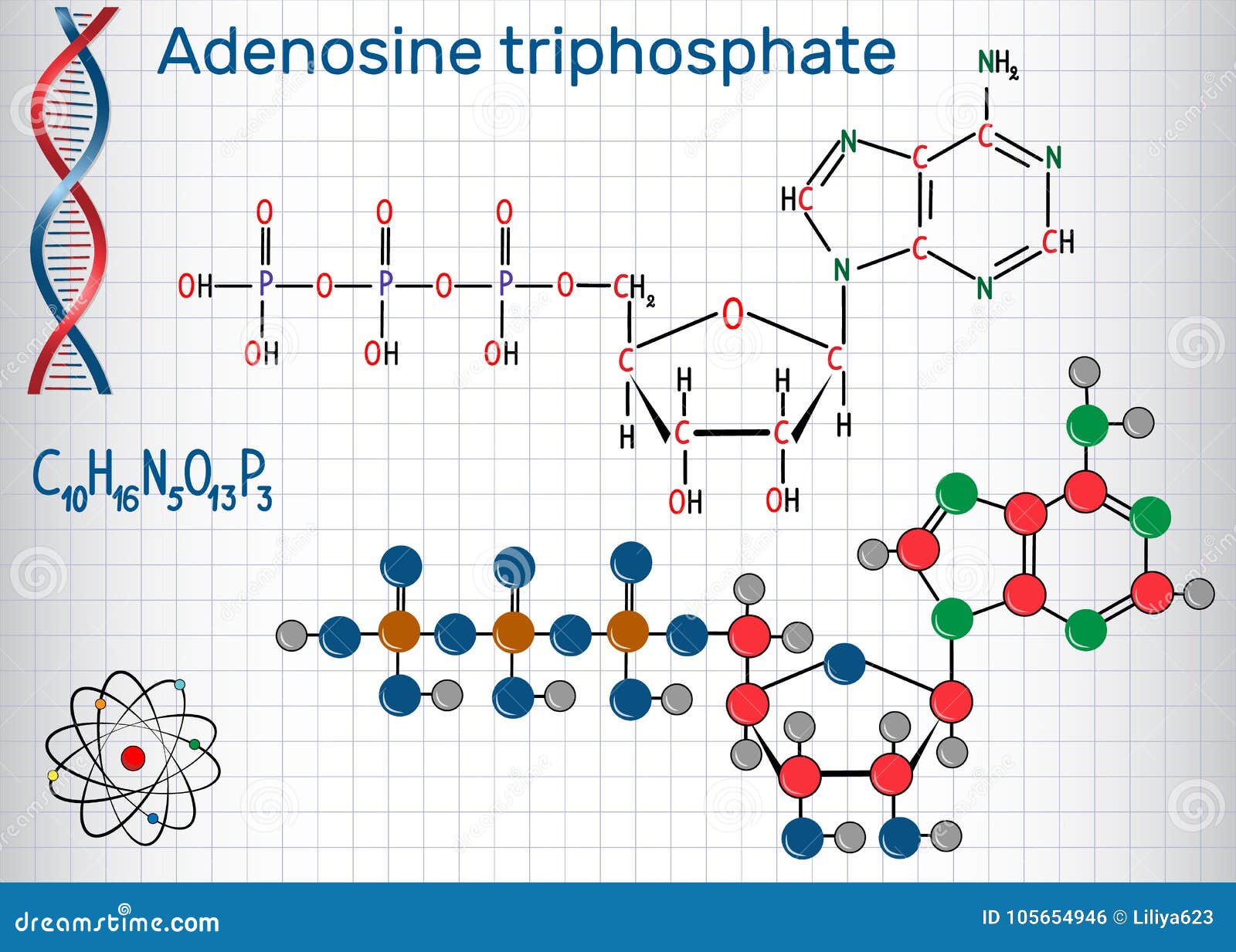
Adenosine triphosphate (atp) is a molecule that provides energy for cellular functions. label the three major components of an atp molecule.
Cellular Function and ATP Energy Production - Kaiyan Medical Red and infrared light promotes melatonin production. This stimulates the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is essential to function properly as it provides our body's cells with energy. This is why red light therapy products are so effective for speeding up the healing process. Chapter 7 Flashcards | Quizlet ATP Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that provides energy for cellular functions. Label three major components of an ATP molecule. three phosphate,ribose,adenine Classify the following statements about the structure of an adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecule as true or false. Reminder: Adenosine diphosphate is abbreviated ADP. 4 Steps of Aerobic Respiration | livestrong Aerobic respiration is a biological process that takes energy from glucose and other organic compounds to create a molecule called Adenosine TriPhosphate (ATP). ATP is then used as energy by nearly every cell in the body -- the largest user being the muscular system.
Adenosine triphosphate (atp) is a molecule that provides energy for cellular functions. label the three major components of an atp molecule.. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function Adenosine triphosphate, also known as ATP, is a molecule that carries energy within cells. It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light), cellular respiration, and fermentation. All living things use ATP. Untitled_document - ATP Adenosine triphosphate a molecule that provides ... energy is released when an atp molecule is converted to an adp (adenosine diphosphate) molecule. bacteria unicellular organisms that contain cells walls andribosomes but not contain a nuclear membrane aroundtheir genetic material or other organelles common to plantand animal cells. carbon dioxide (co 2) a colorless, odorless gas thatis produced … Difference Between ATP and ADP Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an important nucleotide found in cells. ... It is a high energy molecule which has the chemical formula of C 10 H 16 N 5 O 13 P 3. ATP is mainly composed of ADP and a phosphate group. There are three major components found in an ATP molecule namely a ribose sugar, an adenine base and a triphosphate group as shown ... ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate | Boundless Biology | | Course Hero The more bonds in a molecule, the more potential energy it contains. Because the bond in ATP is so easily broken and reformed, ATP is like a rechargeable battery that powers cellular process ranging from DNA replication to protein synthesis. Molecular Structure Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is comprised of the molecule adenosine bound to three ...
BYJUS BYJUS Understanding ATP—10 Cellular Energy Questions Answered The initials ATP stand for adenosine tri-phosphate. This long name translates to a nucleic acid (protein) attached to a sugar and phosphate chain. Phosphate chains are groups of phosphorous and oxygen atoms linked together. One cool fact: ATP closely resembles the proteins found in genetic material. 3. How Does ATP Carry Energy? ATP Flashcards | Quizlet Gravity. ATP. Click card to see definition 👆. Tap card to see definition 👆. Adenosine triphosphate (nucleotide triphosphate) > an energy transfer molecule > everything that we do requires ATP. Sugar (Ribose) Nitrogen-containing base (adenine) Phosphate (THREE of them) Click again to see term 👆. ATP AND BIOLOGICAL ENERGY - Estrella Mountain Community College Adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy currency or coin of the cell pictured in Figfures 1 and 2, transfers energy from chemical bonds to endergonic (energy absorbing) reactions within the cell. Structurally, ATP consists of the adenine nucleotide ( ribose sugar, adenine base, and phosphate group, PO 4-2) plus two other phosphate groups.
Structure of ATP - Learn Insta The Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecule is the nucleotide known in biochemistry as the "molecular currency" of intracellular energy transfer; that is, ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. ATP also plays an important role in the synthesis of nucleic acids. 4 Steps of Aerobic Respiration | livestrong Aerobic respiration is a biological process that takes energy from glucose and other organic compounds to create a molecule called Adenosine TriPhosphate (ATP). ATP is then used as energy by nearly every cell in the body -- the largest user being the muscular system. Chapter 7 Flashcards | Quizlet ATP Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a molecule that provides energy for cellular functions. Label three major components of an ATP molecule. three phosphate,ribose,adenine Classify the following statements about the structure of an adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecule as true or false. Reminder: Adenosine diphosphate is abbreviated ADP. Cellular Function and ATP Energy Production - Kaiyan Medical Red and infrared light promotes melatonin production. This stimulates the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is essential to function properly as it provides our body's cells with energy. This is why red light therapy products are so effective for speeding up the healing process.
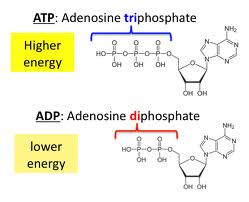

Post a Comment for "45 adenosine triphosphate (atp) is a molecule that provides energy for cellular functions. label the three major components of an atp molecule."