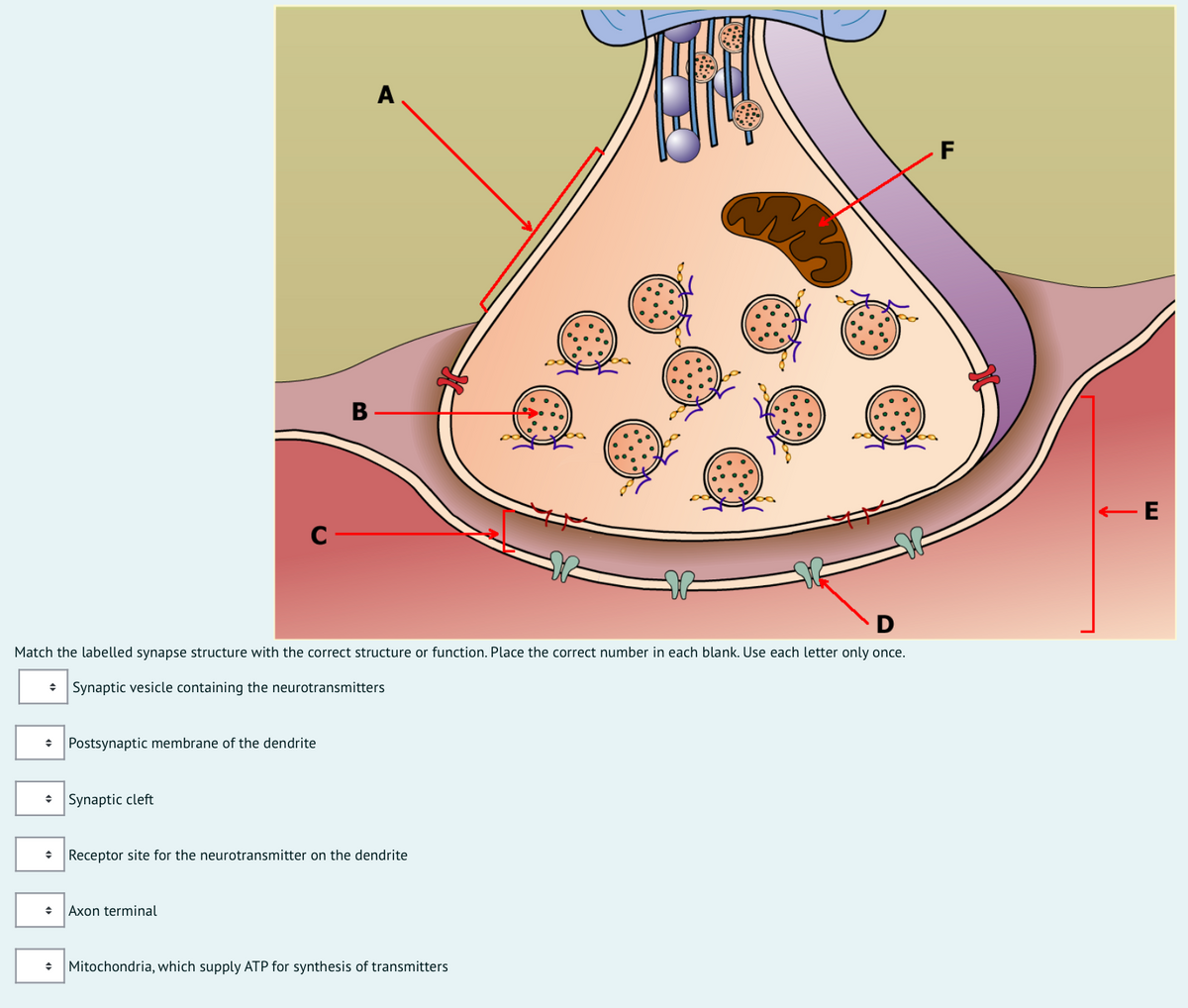
40 click and drag the labels to the correct structure at the chemical synapse.
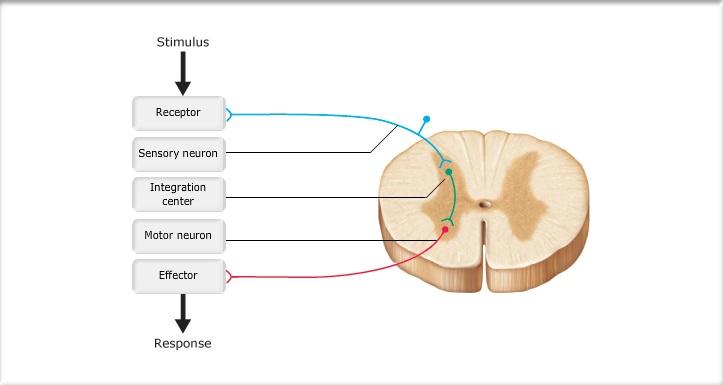
Muscle Contraction - An Interactive Tutorial.docx - Muscle... Label the following structures on the neuromuscular junction diagram below. Click the image, and then click "Edit" below the image. Label the diagram and then click "Save and Close". Click and drag the labels to the correct places. Neuron Sarcolemma Node of Ranvier Myelin Sheath Motor end plate Synaptic Cleft ACh Vesicle ACh Receptor ... Chpt. 1, 3, 24, and 9 HW - Weebly Blood glucose becomes high --> Pancreas releases insulin -->Insulin binds to receptors on target cells --> cells take in glucose --> Blood glucose returns to normal 6. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. (from left to right) Stimulus, receptor, input, control center, output, response, balance (middle) 7.
Practice Final Exam for A&P 1 Mini session with Dr. Hoover *Click and drag the labels into the appropriate box to identify whether or not it is a possible function of the connective tissue component of a muscle based on some of the current theories. Function of connective tissue: -Aids in elastic recoil of muscle -Prevents the muscle from over stretching -Helps the muscle function more efficiently
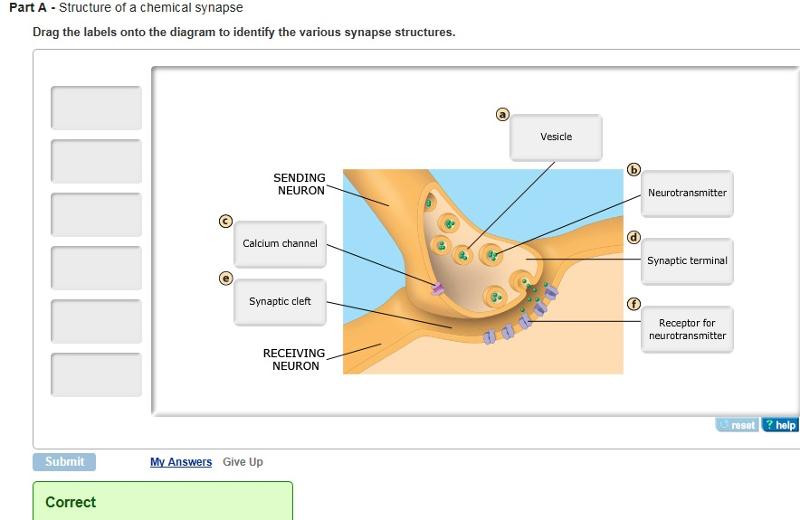
Click and drag the labels to the correct structure at the chemical synapse.
Wk 5 Ch 11 Flashcards | Quizlet the sum of the electrical and concentration gradients for that ion An ion's electrochemical gradient consists of two parts. The first part, the electrical gradient, is a consequence of the membrane potential. For negative membrane potential values, positively-charged ions (like K+ and Na+) tend to enter the cell. Chapter 13 - Synapses - Michael D. Mann The majority of the synapses in the vertebrate central nervous system are of the axosomatic and axodendritic types and of the chemically transmitting type. It is therefore a small wonder that chemical transmission is the most thoroughly understood. There are now many reports of gap junctions and presumed electrotonic coupling between neurons in Molecular Knowledge Systems: Getting Started Using Cranium 0315 Click the left mouse button on the Chemicals Chapter tab located at the top of the window. Cranium displays a page of the Chemicals Chapter. ... Drag the mouse downward to the fifteenth row and release the mouse button. Rows two through fifteen will now be highlighted. ... Scroll the data pane to the Chemical Structure section, located near the ...
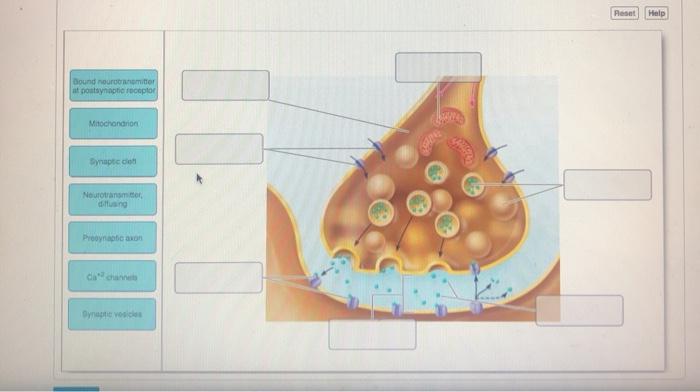
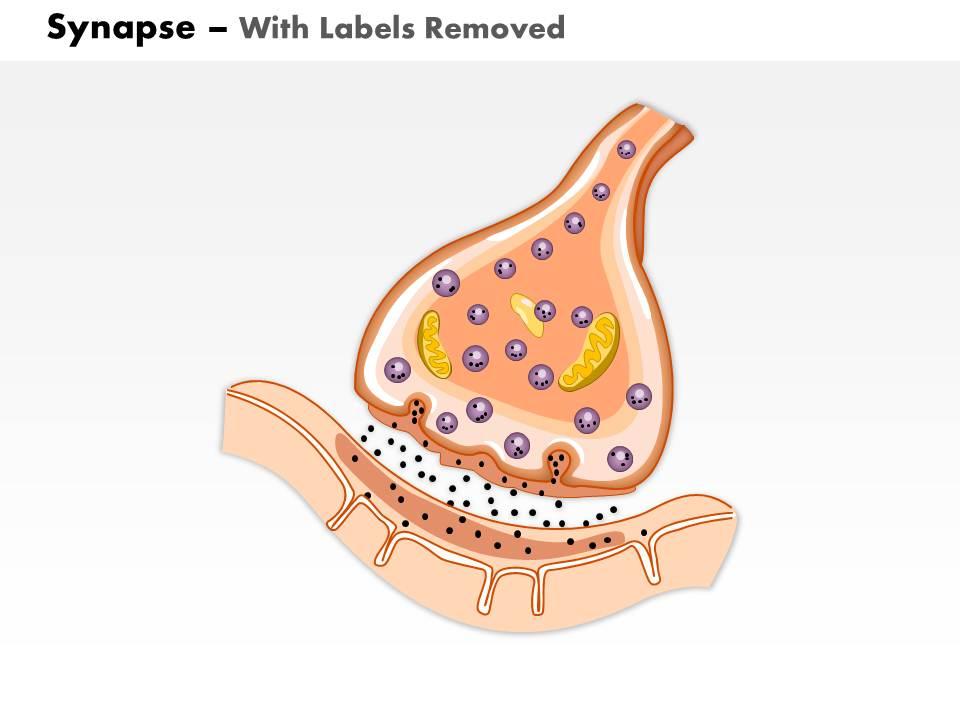
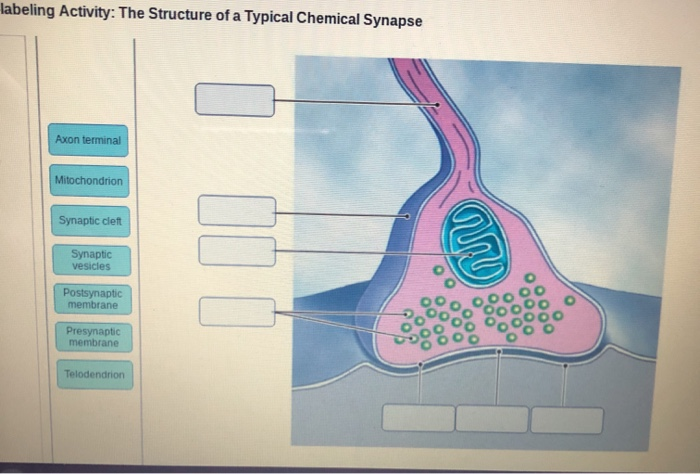
Click and drag the labels to the correct structure at the chemical synapse.. Imagine you changed the concentration of k outside a Pages 8 ; This preview shows page 4 - 7 out of 8 pages.preview shows page 4 - 7 out of 8 pages. Neurophysiology Activities flashcards Easy.pdf - Course Hero Drag and drop the descriptive labels ofevents into the correct sequence at the chemical synapse. 1. Action potential sweeps down presynaptic axon 2. Calcium channels open in axon terminal. back 51 3. Synaptic vesicles fuse and exocytize neurotransmitter 4. Diffusion of neurotransmitter into extracellular fluid separating two neuron's membranes 5. Solved Click and drag the labels to the correct structure at - Chegg Expert Answer synaptic transmission it is a release of neurotrneu … View the full answer Transcribed image text: Click and drag the labels to the correct structure at the chemical synapse. View Available Hint (s) Reset Presynaptic axon Synaptic vesicles Cat channels Bound neurotransmitter af postsynaptio receptor Synaptic clen Meochondrion Bioflix activity how neurons work resting potential - Course Hero To review the structure of a chemical synapse, watch this BioFlix animation: How Synapses Work. Part A - Structure of a chemical synapse Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the various synapse structures.
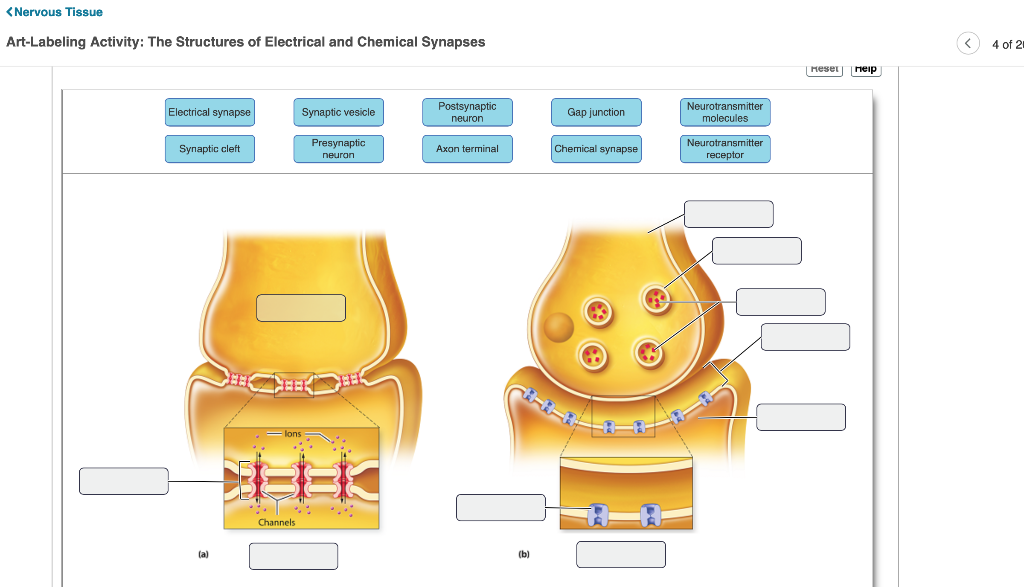
Ch 11 A&P HW Flashcards | Quizlet Drag and drop the descriptive labels of events into the correct sequence at the chemical synapse. action potential sweeps down presynaptic axon, calcium channels open in axon terminal, synaptic vesicles fuse and exoctytize neurotransmitter, diffusion of neurotransmitter into extracellular fluid separating two neurons membranes, graded potential at postsynaptic membrane. Chapter 11 Homework Flashcards | Quizlet Drag the appropriate labels to their targets. Note that pink labels should go in pink targets, blue labels should go in blue targets, and green labels should go in green targets. For each of the following, indicate whether the condition will cause the membrane potential to become more positive, more negative, or largely unchanged when compared to the normal physiological resting membrane potential. CH 11 Assignment 2021-22 Introduction to Physiology. Language ... - StuDocu Part C Click and drag the labels to the correct structure at the chemical synapse. Hint 1. Diffusion and synaptic transmission In the process of synaptic transmission, diffusion happens outside of the neurons. Within a neuron, the neurotransmitters that will be used to send a message from one neuron to the other are packaged within vesicles. Hint 2. PDF In this chapter, you will learn that - Pearson In this chapter, we first examine the structure and function of skeletal muscle. Then we consider smooth muscle more briefly, largely by comparing it with skeletal muscle. We describe cardiac muscle in detail in Chapter 18, but for easy comparison, Table 9.3 on pp. 310-311 summarizes the characteristics of all three muscle types.
Solved Part Click and drag the labels to the correct | Chegg.com Anatomy and Physiology questions and answers. Part Click and drag the labels to the correct structure at the chemical synapse View Available Hint) Reset Help Bound nourriter at postsynaptic footor Mitochondrion Dynapte Neurotransmitter dang Pronatan Ovoice Click and drag the labels to the correct structure at the chemical synapse. Week 3: Neurophysiology Flashcards - Quizlet Drag the appropriate labels to their targets. Note that pink labels should go in pink targets, blue labels should go in blue targets, and green labels should go in green targets. For each of the following, indicate whether the condition will cause the membrane potential to become more positive, more negative, or largely unchanged when compared to the normal physiological resting membrane potential. PDF 5. Events Occurring at a Chemical Synapse - Mr. Cribley's Classroom Events Occurring at a Chemical Synapse 1. An action potential occurs in the pre-synaptic neuron. 2. The action potential reaches the synaptic knob at the axon terminal. 3. ++This causes opening of voltage-gated Ca channels in the synaptic knob. 4. ++Ca rushes into the synaptic knob. 5. The 9 parts of a neuron (and their functions) - medical - 2022 Nissl substance. 7. Ranvier's nodules. 8. Synaptic buttons. 9. Axonal cone. Bibliographic references. Neurons are a type of cells in our body that are incredibly specialized on a morphological level. and physiological in fulfilling an essential function: transmitting information throughout the body.
A&P Chapter 11 Nervous System 2 Homework - GraduateWay Determine whether the following descriptions apply to sensory nerves, motor nerves, or mixed nerves (both sensory and motor). Place each cranial nerve label in the appropriate category, describing its function. Label the terminal branches of the brachial plexus. Label the structures of the central nervous system and their protective structures.
A molecule that carries information across a synaptic 51Drag and drop the descriptive labels of events into the correct sequence at the chemical synapse. 1. Action potential sweeps down presynaptic axon 2. Calcium channels open in axon terminal. 3. Synaptic vesicles fuse and exocytize neurotransmitter 4. Diffusion of neurotransmitter into extracellular fluid separating two neuron'smembranes 5.
Exam 2 Key - University of North Florida D. Both the electrical and chemical gradients for Cl- ions favor outward movement of Cl- ions. 7. Place the following steps in an action potential in the correct order. 1. Sodium channels become inactivated and potassium channels are opened. 2. Sodium and potassium channel gates are closed; membrane potential is -60mV. 3.
Chapter 11 - Neurophysiology Activities Flashcards - Easy Notecards Choose the correct order of these events below. (a) Voltage-gated calcium channels open (b) Neurotransmitter binds to receptors (c) Action potential arrives at axon terminal (d) Neurotransmitter is removed from the synaptic cleft (e) Neurotransmitter released into synaptic cleft (f) Graded potential generated in postsynaptic cell
A&P Pearson Homework 11 - Study Flashcards - Quizlet Drag the appropriate labels to their targets. Note that pink labels should go in pink targets, blue labels should go in blue targets, and green labels should go in green targets. For each of the following, indicate whether the condition will cause the membrane potential to become more positive, more negative, or largely unchanged when compared to the normal physiological resting membrane potential.
Structure of Chemical Synapses | SynapseWeb The most common types of synapses in the brain use chemicals (more specifically, neurotransmitters) to communicate between neurons. These are called chemical synapses. A presynaptic element, an axon, and a postsynaptic element, for example a dendritic spine, are in close apposition at the synapse but not in direct contact.
Molecular Knowledge Systems: Getting Started Using Cranium 0315 Click the left mouse button on the Chemicals Chapter tab located at the top of the window. Cranium displays a page of the Chemicals Chapter. ... Drag the mouse downward to the fifteenth row and release the mouse button. Rows two through fifteen will now be highlighted. ... Scroll the data pane to the Chemical Structure section, located near the ...
Chapter 13 - Synapses - Michael D. Mann The majority of the synapses in the vertebrate central nervous system are of the axosomatic and axodendritic types and of the chemically transmitting type. It is therefore a small wonder that chemical transmission is the most thoroughly understood. There are now many reports of gap junctions and presumed electrotonic coupling between neurons in
Wk 5 Ch 11 Flashcards | Quizlet the sum of the electrical and concentration gradients for that ion An ion's electrochemical gradient consists of two parts. The first part, the electrical gradient, is a consequence of the membrane potential. For negative membrane potential values, positively-charged ions (like K+ and Na+) tend to enter the cell.
























Post a Comment for "40 click and drag the labels to the correct structure at the chemical synapse."